
In the evolving landscape of software development, one of the most significant challenges developers face is dealing with misleading bug reports. This issue has been amplified with the rise of AI-generated reports that can waste valuable development time and resources. By examining these reports, we can identify common software development mistakes and learn how to avoid them in our own projects.
The Problem with AI-Generated Bug Reports
Software maintainers are increasingly facing a deluge of AI-generated bug reports that claim to identify critical vulnerabilities but often contain misleading or entirely fabricated information. These reports can appear technically correct at first glance, using appropriate terminology and formatting, but fail to demonstrate actual issues in the codebase they claim to affect.
A prime example of this phenomenon involves the maintainer of curl, a widely-used command-line tool for transferring data with URLs. The maintainer has been inundated with AI-generated bug reports claiming to find critical vulnerabilities in the curl codebase. Many of these reports follow a similar pattern: they appear technically sound, include appropriate technical details, and even assign severity ratings like CVSS scores - yet they fail to demonstrate actual vulnerabilities in the curl codebase.
Common Mistakes in Software Development Revealed by These Reports
By analyzing these misleading bug reports, we can identify several common mistakes that developers should avoid in their own practices:
- Failing to verify that code actually calls the functions it claims to affect
- Not testing proof-of-concept code before submitting bug reports
- Misunderstanding fundamental concepts like buffer overflows and memory management
- Relying too heavily on tools like ASAN without understanding their output
- Assigning severity ratings without proper verification of impact
- Creating technically correct but contextually irrelevant demonstrations
- Submitting reports without sufficient domain knowledge
Anatomy of a Misleading Bug Report
Let's examine a typical AI-generated bug report to understand what makes it problematic. These reports often follow a predictable structure:
- Claims of a critical vulnerability (often with exaggerated CVSS scores)
- Technical jargon that appears correct but lacks contextual relevance
- Code snippets that demonstrate issues unrelated to the claimed vulnerability
- Stack traces or error outputs that don't actually involve the target software
- Excessive use of emojis or formatting that suggests automated generation
- Vague descriptions of impact without specific attack vectors
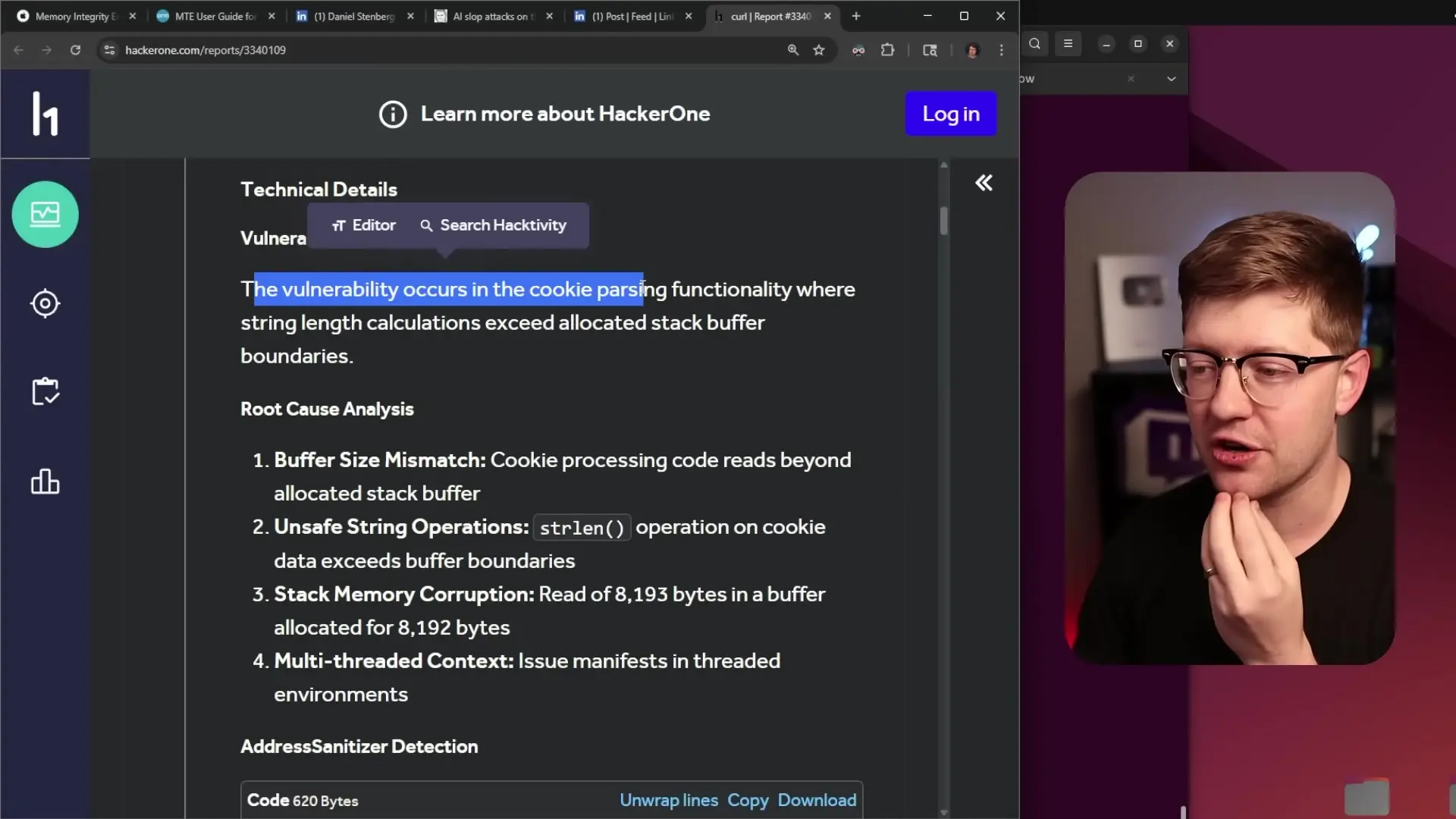
In one particularly notable example, a report claimed to identify a "critical stack-based buffer overflow vulnerability in Curl's cookie parsing mechanism that can lead to remote code execution." However, the proof-of-concept code provided did not actually call any curl functions. Instead, it demonstrated a basic buffer overflow in standard C string handling functions unrelated to curl's implementation.
The Impact on Software Development Teams
These misleading reports create significant challenges for software development teams:
- Wasted time triaging and investigating non-existent issues
- Reduced trust in legitimate bug reports and vulnerability disclosures
- Potential security risks if real vulnerabilities are missed among the noise
- Increased maintainer burnout and frustration
- Diverted resources from actual development and improvement tasks
According to the curl maintainer, triaging these reports can take multiple team members up to 30-60 minutes each, representing a significant drain on resources that could be better spent on actual development work.
Tools and Techniques That Can Be Misused
Many of these misleading reports leverage legitimate development tools, but in ways that demonstrate a lack of understanding about their proper use:
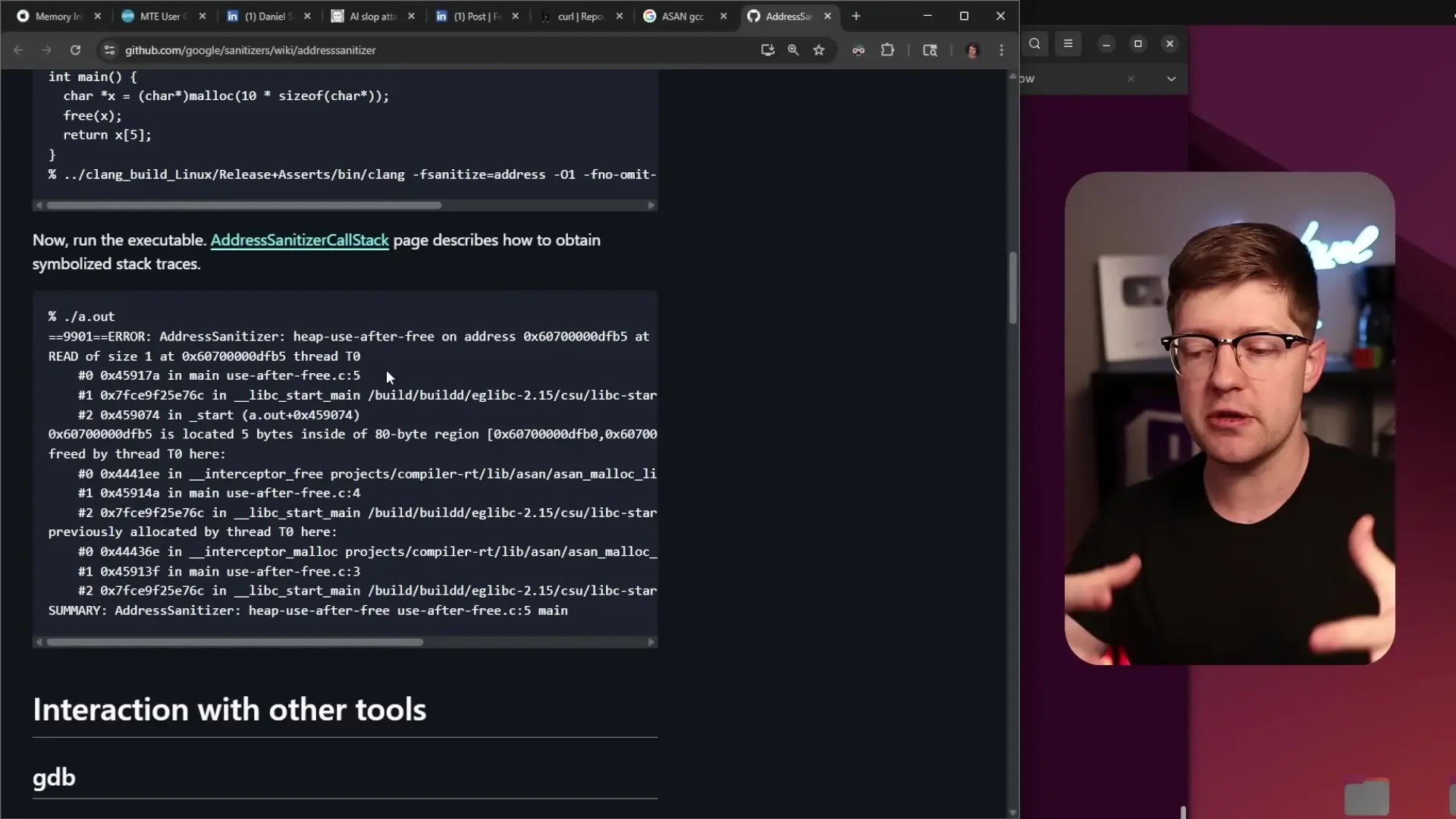
- Address Sanitizer (ASAN): A valuable tool for detecting memory errors, but reports often misinterpret its output
- String length functions: Basic C functions like strlen() are often used incorrectly in demonstrations
- Memory allocation: Reports frequently show basic memory allocation mistakes unrelated to the software being reported
- CVSS scoring: Vulnerability scoring systems are applied without proper understanding of actual impact
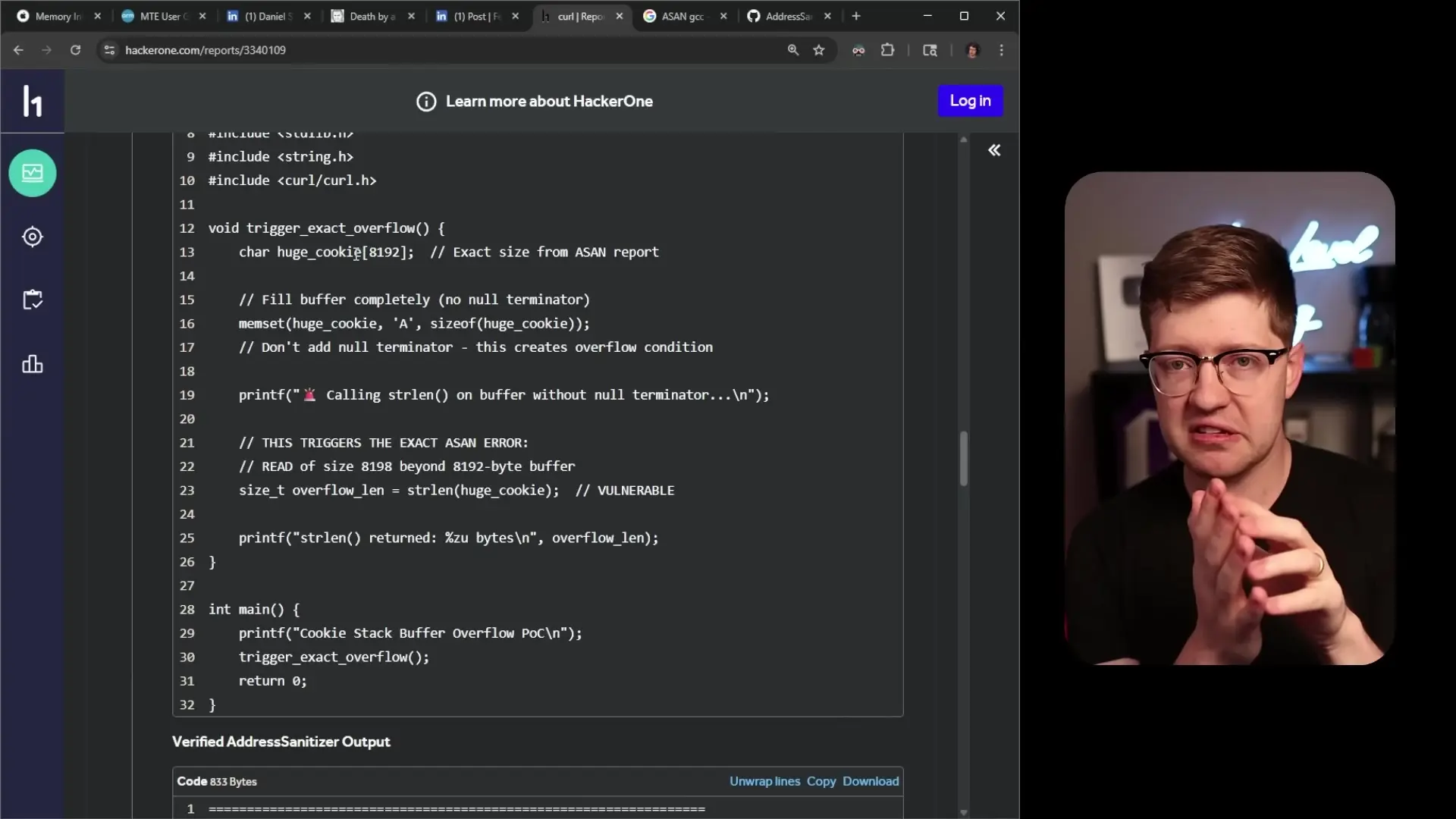
// Example of misleading code often found in these reports
char huge_cookie[8192];
memset(huge_cookie, 'A', sizeof(huge_cookie));
// No null termination, which will cause issues with strlen
size_t length = strlen(huge_cookie); // This will read past the buffer
// But this has nothing to do with curl's implementationIn the example above, the code demonstrates a basic C programming error (not null-terminating a string before calling strlen), but doesn't actually involve or test the software being reported as vulnerable.
Best Practices for Software Engineers
To avoid making similar mistakes in your own development and security work, consider these best practices:
- Always verify that your test cases actually exercise the code you're claiming has issues
- Understand the tools you're using - don't just rely on their output without comprehension
- When reporting bugs, be specific about which functions are affected and how
- Test your proof-of-concept thoroughly before submission
- If using AI tools to assist with development or security work, verify their output manually
- Develop a deep understanding of memory management and other fundamental concepts
- Contribute to open-source projects to gain practical experience with real-world codebases
The Importance of Understanding Fundamentals
Many of the common mistakes in software development revealed by these misleading reports point to a fundamental issue: a lack of understanding of core programming concepts. This highlights the importance of mastering the basics of computer science and programming languages like C, particularly when working on security-sensitive applications.
Understanding memory management, buffer boundaries, string operations, and how libraries interact is essential for both finding real vulnerabilities and avoiding false reports. This knowledge helps developers write more secure code and contribute meaningfully to the security community.
Conclusion: Learning from Software Development Mistakes
While AI-generated bug reports can be frustrating for maintainers, they provide valuable lessons about common mistakes in software development. By understanding these patterns, developers can improve their own practices and avoid similar pitfalls.
The key takeaway is that thorough understanding, verification, and testing are essential in software development - whether you're writing code, reporting bugs, or maintaining a project. These principles help create more reliable, secure software and foster a more productive development community.
As software development continues to evolve alongside AI tools, maintaining these fundamental skills and practices becomes even more important. By learning from these mistakes, we can build better software and contribute more effectively to the projects we care about.
Let's Watch!
7 Common Software Development Mistakes Revealed by AI-Generated Bug Reports
Ready to enhance your neural network?
Access our quantum knowledge cores and upgrade your programming abilities.
Initialize Training Sequence