
Building applications with real-time synchronization capabilities has traditionally required complex backend setups and custom solutions. Zero, a sync engine from the Replicash team, offers a streamlined approach to this challenge by providing a client-side cache that synchronizes data across browsers in real-time. In this guide, we'll explore how to implement Zero in a React application to create a seamless user experience with instant database updates.
What Makes Zero Different from Other Sync Engines?
Zero stands out from other synchronization solutions by offering a unique combination of features that simplify real-time data management:
- Client-side cache that syncs directly to connected clients
- Built-in query language that eliminates the need for a custom backend
- Real-time updates across multiple browsers and tabs simultaneously
- Direct integration with PostgreSQL databases
Setting Up Your Database for Zero
The first step in implementing Zero is setting up a PostgreSQL database that can efficiently track and sync changes. Here's how to get started:
- Create a PostgreSQL database (Neon is recommended for its cloud capabilities)
- Enable logical replication to efficiently track and sync changes
- Connect with pooling turned off to maintain a persistent connection
- Add test data to your database to verify functionality
Logical replication is crucial as it allows Zero to efficiently track changes in your database. With pooling turned off, the connection remains persistent, which is necessary for real-time synchronization.
Configuring Zero Cache
Once your database is ready, the next step is to set up Zero Cache, which comes with the Zero package. Configuration is primarily done through environment variables.
// Example environment variables for Zero Cache configuration
ZERO_DATABASE_URL=postgres://user:password@hostname:port/database
ZERO_REPLICATION_SLOT=zero_replication
ZERO_PUBLICATION=zero_publicationCreating a Schema File
A critical aspect of using Zero is creating a schema file that provides type safety, defines relationships, and establishes permissions. By default, Zero denies all access to database operations, so you must explicitly define permissions.
If you're already using Drizzle or Prisma in your project, you can automatically generate schemas using integration projects designed for this purpose, saving significant development time.
// Example schema definition for Zero
export const schema = {
models: {
users: {
id: { type: 'uuid', primaryKey: true },
name: { type: 'string' },
email: { type: 'string' }
},
posts: {
id: { type: 'uuid', primaryKey: true },
title: { type: 'string' },
content: { type: 'string' },
userId: { type: 'uuid', references: 'users.id' }
}
},
permissions: {
users: {
read: true,
create: true,
update: true
},
posts: {
read: true,
create: true,
update: true
}
}
}Setting Up the Zero Client in React
Integrating Zero with React is straightforward thanks to dedicated React hooks. Here's how to set it up:
- Install the Zero client package
- Instantiate the Zero client class with required options
- Wrap your application in the Zero provider component
- Use the provided hooks to make queries and mutations
// Setting up Zero client in a React application
import { ZeroProvider, createZeroClient } from '@zero-tech/client-react';
// Create the client instance
const zeroClient = createZeroClient({
databaseURL: process.env.ZERO_DATABASE_URL,
schema: schema,
token: 'your-auth-token' // Optional for authentication
});
// Wrap your app with the provider
function App() {
return (
<ZeroProvider zero={zeroClient}>
<YourApplication />
</ZeroProvider>
);
}With the provider in place, you can now use Zero's hooks in your components to interact with your data:
// Example component using Zero hooks
import { useZero, useQuery } from '@zero-tech/client-react';
function UserList() {
const zero = useZero();
const { data: users, loading } = useQuery(zero.db.users.findMany());
const updateUserName = async (userId, newName) => {
await zero.db.users.update({
where: { id: userId },
data: { name: newName }
});
};
if (loading) return <div>Loading...</div>;
return (
<div>
{users.map(user => (
<div key={user.id}>
<input
value={user.name}
onChange={(e) => updateUserName(user.id, e.target.value)}
/>
</div>
))}
</div>
);
}Real-Time Updates Across Multiple Browsers
Once properly configured, Zero enables real-time updates across multiple browsers and tabs. Changes made in one tab are instantly reflected in all connected clients, regardless of the browser being used. This functionality is particularly valuable for collaborative applications, dashboards, and any scenario where data consistency across multiple clients is essential.
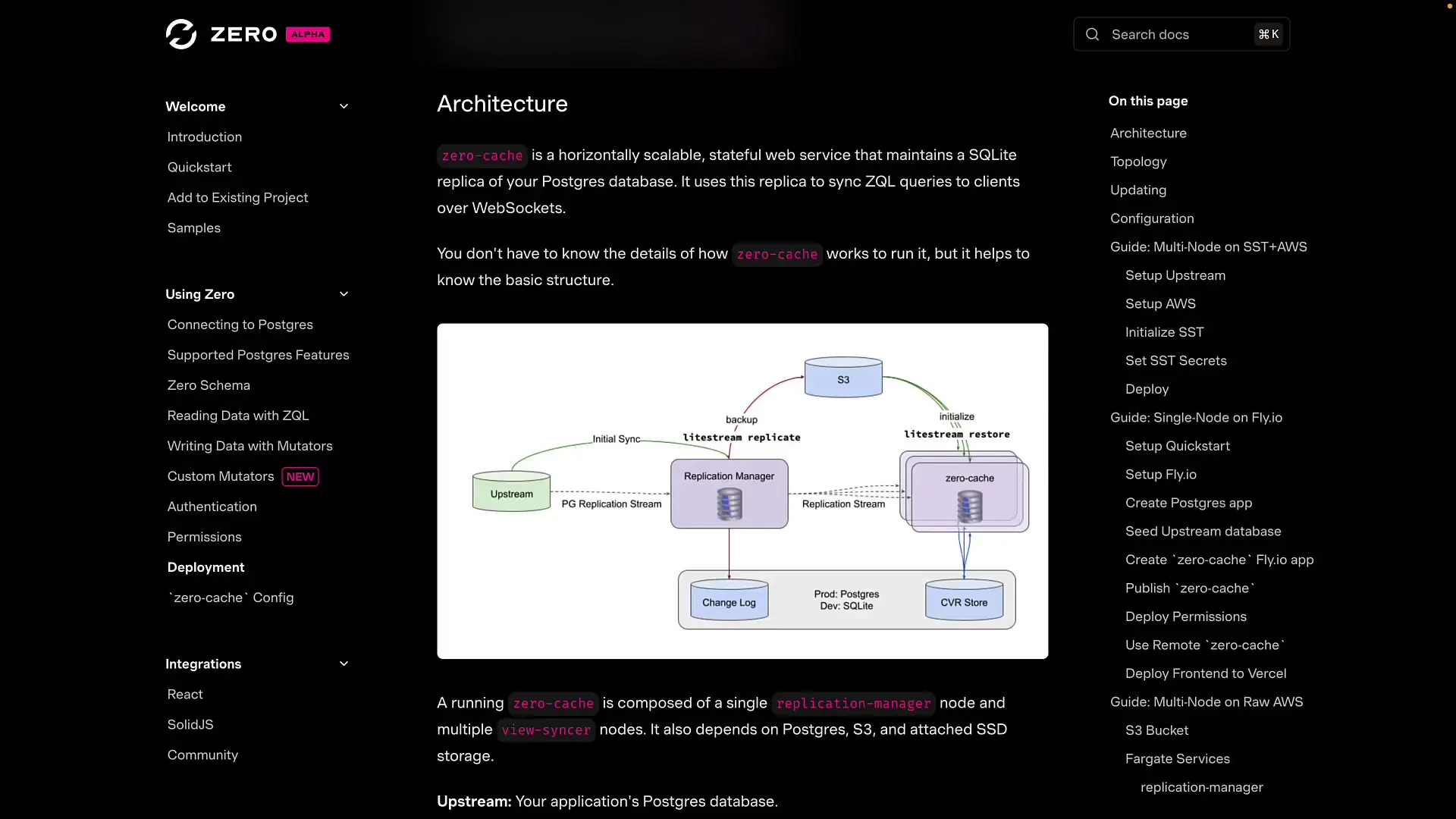
Deployment Considerations
While Zero simplifies the development of real-time applications, deployment requires careful planning. The recommended approach is to use SST (Serverless Stack), though other deployment options are possible with additional configuration.
Advanced Zero Features
For developers looking to take Zero to the next level, several advanced features are worth exploring:
- Custom mutators for complex data transformations
- Authentication integration for secure data access
- Optimistic UI updates for improved user experience
- Conflict resolution strategies for concurrent edits
Conclusion
Zero represents a significant advancement in the field of real-time database synchronization. Despite being in alpha, it already offers impressive capabilities that simplify building applications with instant updates across multiple clients. The initial setup process may be somewhat involved, but the resulting functionality—real-time synchronization without a custom backend—makes it well worth the effort for many use cases.
As Zero continues to mature, we can expect further improvements in documentation, setup processes, and additional features. For developers building collaborative applications or any system requiring real-time data consistency, Zero is definitely a technology worth watching and experimenting with today.
Let's Watch!
Build Lightning-Fast React Apps with Zero: Real-Time Database Sync Across Browsers
Ready to enhance your neural network?
Access our quantum knowledge cores and upgrade your programming abilities.
Initialize Training Sequence