
A major npm supply chain breach has recently unfolded, potentially affecting millions of developers and projects worldwide. The attack targeted popular packages that collectively see over 2.6 billion downloads weekly, highlighting critical vulnerabilities in the open-source ecosystem that all developers should be aware of.
The Anatomy of the Attack
The breach began when a well-known npm maintainer, Josh Junon (also known as Kicks), fell victim to a phishing attack. The attackers successfully bypassed his two-factor authentication and gained control of his account. With this access, they injected malicious code into at least 18 widely trusted packages, including popular utilities like chalk, debug, strips-anc, and styles.

The compromised packages form the foundation of countless JavaScript projects and tools like Babel and ESLint. This incident demonstrates how a single compromised account can potentially affect the entire npm ecosystem, which serves as the backbone for modern web development.
The Malicious Payload: A Crypto Clipper
The malware injected into these packages was identified as a crypto clipper—a particularly insidious type of malware designed to intercept cryptocurrency transactions. When active on a user's system, it monitors for Web3 or crypto transactions in the browser and silently replaces the intended wallet addresses with addresses controlled by the attackers.

What makes this attack particularly dangerous is that it operates without triggering obvious alarms. Users might not notice the address swap until after funds have been transferred to the attacker's wallet. Fortunately, the attack was detected quickly by Iikido, a Belgian security company, limiting the actual financial damage to less than $50 in stolen funds.
Immediate Response and Mitigation
The npm security team responded swiftly, removing the compromised package versions within approximately an hour of detection. However, the potential for lingering impact remains due to cached lock files and indirect dependencies that might still contain the malicious code.
This incident highlights a critical vulnerability in the npm ecosystem: the vast trust network that allows a single compromised account to potentially affect billions of package downloads. Despite the minimal financial damage in this case, the potential for catastrophic impact was significant.
How to Protect Your Projects from npm Security Vulnerabilities
If you're a JavaScript developer or manage projects that use npm dependencies, here are essential steps to protect yourself and your projects from similar npm security vulnerabilities:
- Audit your packages regularly using npm audit to identify and address security issues
- Clean your local caches with npm cache clean --force to remove potentially compromised packages
- Reinstall dependencies to ensure you're using clean, updated versions
- Implement dependency pinning and lockfiles to prevent automatic updates without review
- Consider using tools that detect malicious package changes and flag suspicious code
# Check for vulnerabilities in your project
npm audit
# Clean local cache to remove potentially compromised packages
npm cache clean --force
# Reinstall dependencies
npm ci # If you have a package-lock.json
# or
npm install # To generate a new lock fileSpecial Considerations for Cryptocurrency Applications
If you develop applications that interact with cryptocurrency or Web3 technologies, additional precautions are necessary:
- Use hardware wallets whenever possible to approve transactions
- Implement multiple verification steps for wallet addresses
- Double-check destination addresses before approving any transaction
- Consider implementing address validation systems that detect unexpected changes
Broader Implications for Open Source Security
This incident raises important questions about the security model of open-source package ecosystems. When a single compromised account can potentially affect billions of downloads, we must reconsider our approach to supply chain security.
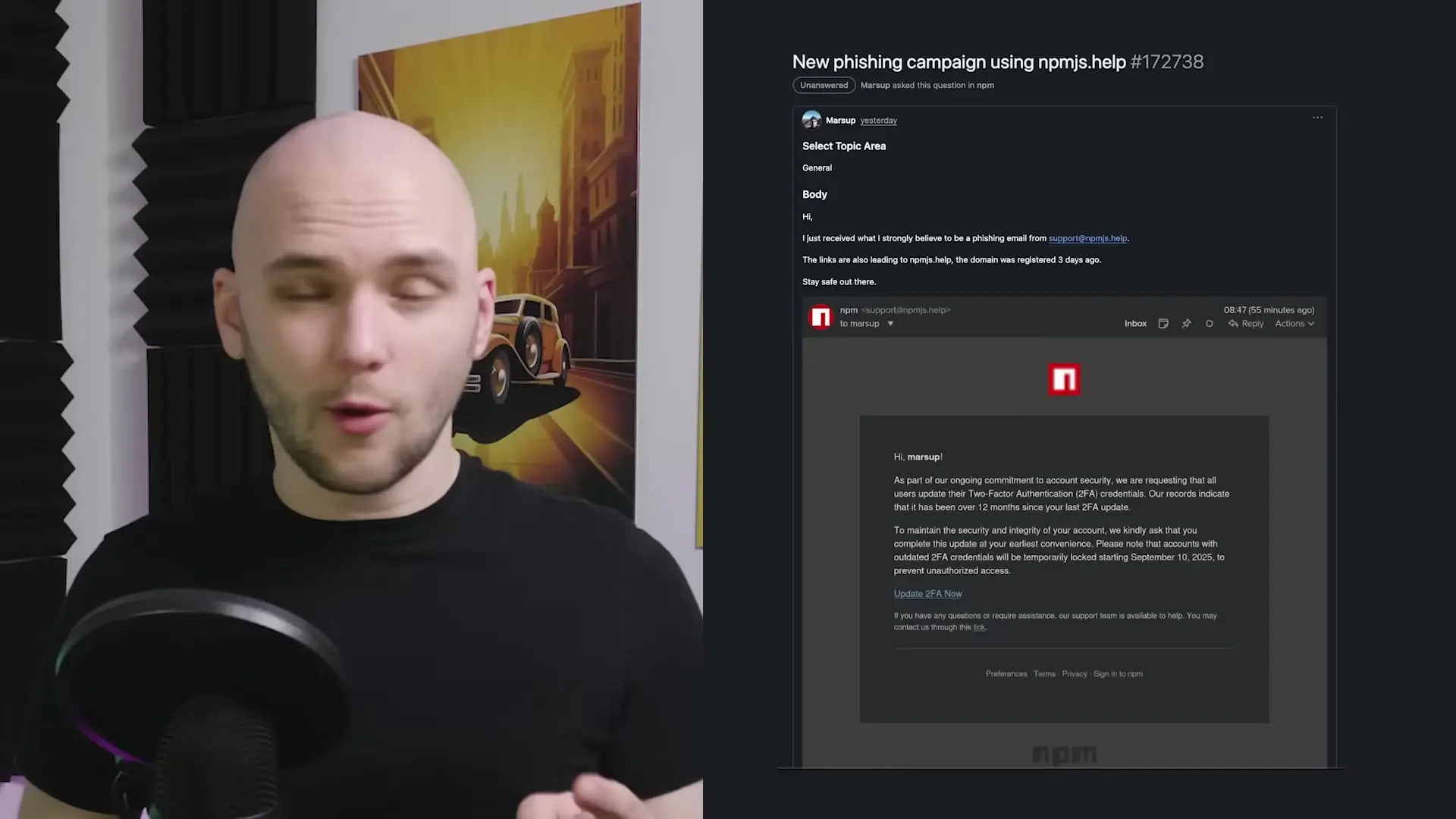
The attack demonstrates that even trusted contributors with proper security practices can become unwitting vectors for malware distribution. One successful phishing email was enough to potentially compromise millions of downstream projects and users.
Long-term Solutions for npm Security Issues
To address npm security vulnerabilities more comprehensively, the JavaScript ecosystem needs to consider several structural improvements:
- Implement more robust multi-party authorization for critical package updates
- Develop better automated scanning for suspicious code patterns in package updates
- Create more granular permission systems for package maintainers
- Establish industry standards for supply chain security in open-source ecosystems
- Encourage the use of signed packages and verified builds
Conclusion: Vigilance is Key
This npm security breach serves as a stark reminder that the open-source ecosystem, while powerful and enabling, carries inherent risks that require ongoing vigilance. The incident highlights how quickly malicious code can propagate through the dependency network when a trusted account is compromised.
For developers and organizations, this underscores the importance of implementing robust security practices, regularly auditing dependencies, and staying informed about potential npm vulnerabilities. By taking proactive measures and adopting a security-first mindset, we can collectively work to minimize the impact of such supply chain attacks in the future.
Remember that security is a continuous process, not a one-time effort. Regular audits, careful validation of dependencies, and staying informed about security best practices are essential components of maintaining secure applications in today's interconnected development ecosystem.
Let's Watch!
Major NPM Security Breach: 2.6B Weekly Downloads Affected by Crypto Clipper
Ready to enhance your neural network?
Access our quantum knowledge cores and upgrade your programming abilities.
Initialize Training Sequence