
Master JavaScript Arithmetic Operators: Essential Guide for Beginners
Master JavaScript Arithmetic Operators: The Complete Guide for Web Developers
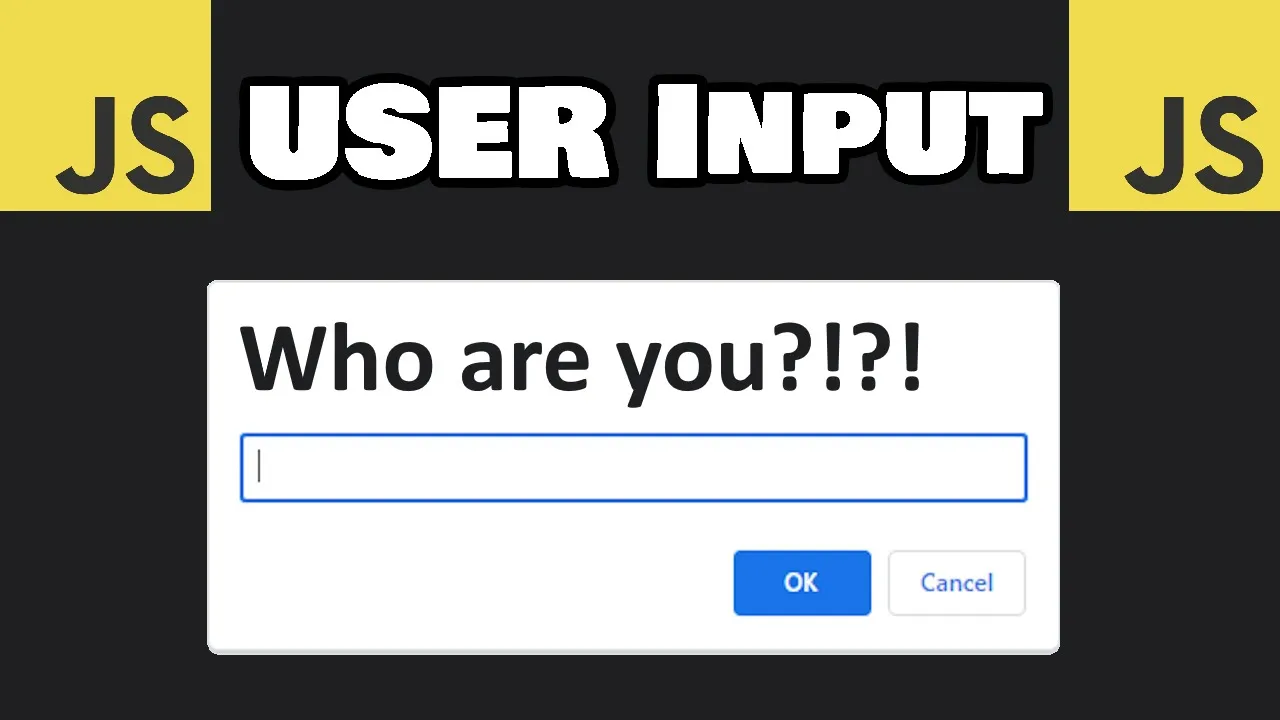
Accepting and processing user input is a fundamental skill for any JavaScript developer. Whether you're building a simple form or a complex web application, knowing how to effectively capture what users type is essential. In this guide, we'll explore two distinct approaches to accepting user input in JavaScript: the quick window.prompt method and the more professional HTML form-based approach.
The window.prompt() method provides a straightforward way to collect user input with minimal code. This approach creates a dialog box that pauses script execution until the user responds by entering text and clicking OK or Cancel.
Let's start by implementing a basic prompt that asks for a username:
// Declare our variable first
let username;
// Assign the value from the prompt
username = window.prompt("What's your username?");
// Do something with the input
console.log(username);When this code runs, it will display a dialog box asking for the username. After the user enters their name and clicks OK, the value will be stored in the username variable and then logged to the console.

You can also combine the declaration and assignment in a single line for more concise code:
// Combined declaration and assignment
let username = window.prompt("What's your username?");
console.log(username);For a more professional and customizable user input experience, using HTML form elements with JavaScript event handling is the preferred approach. This method allows for better styling, validation, and a smoother user experience.
First, we need to create the HTML structure with a text input and a submit button:
<h1 id="myH1">Welcome</h1>
<label for="myText">Username</label>
<input type="text" id="myText">
<br><br>
<button id="mySubmit">Submit</button>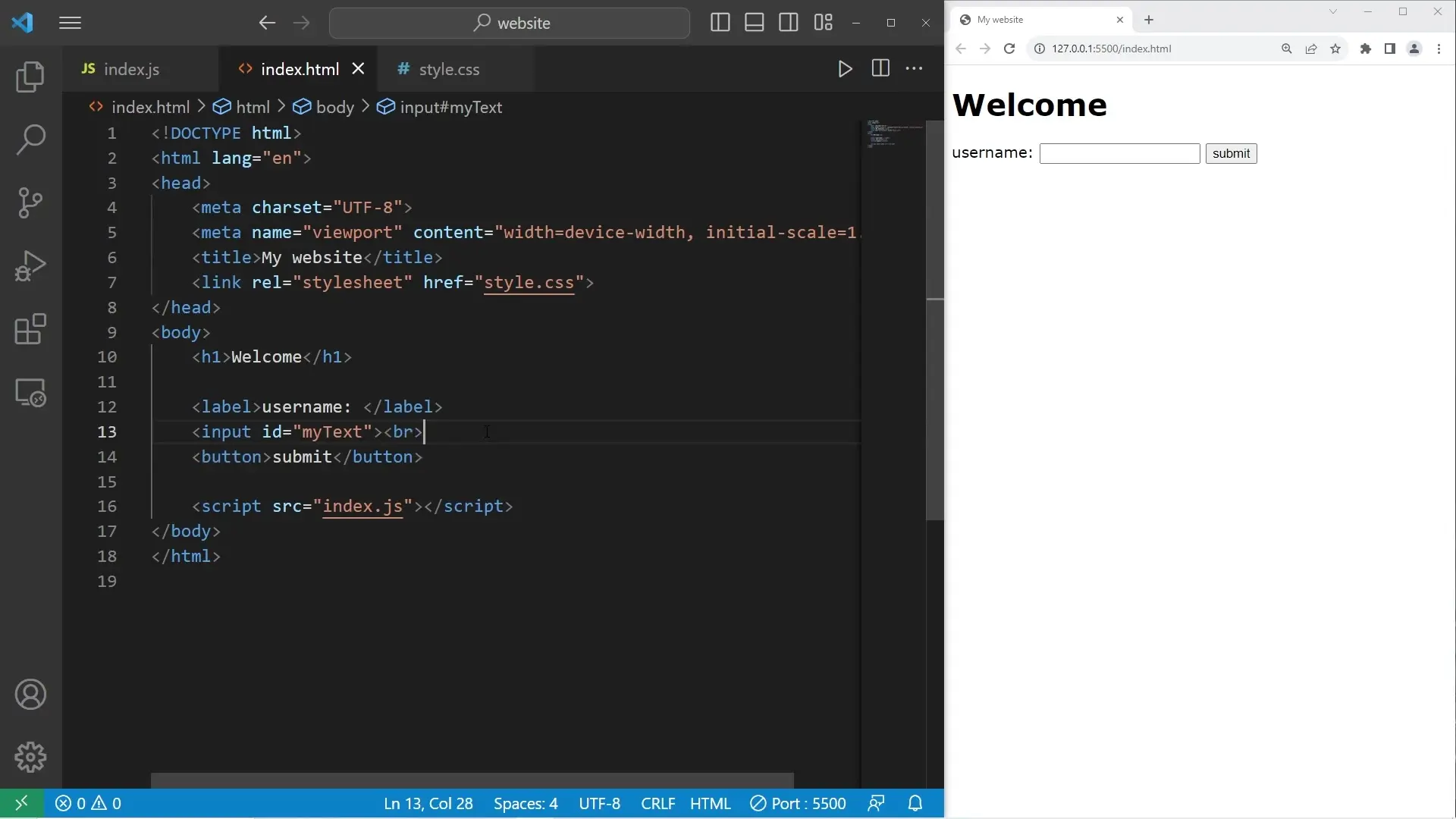
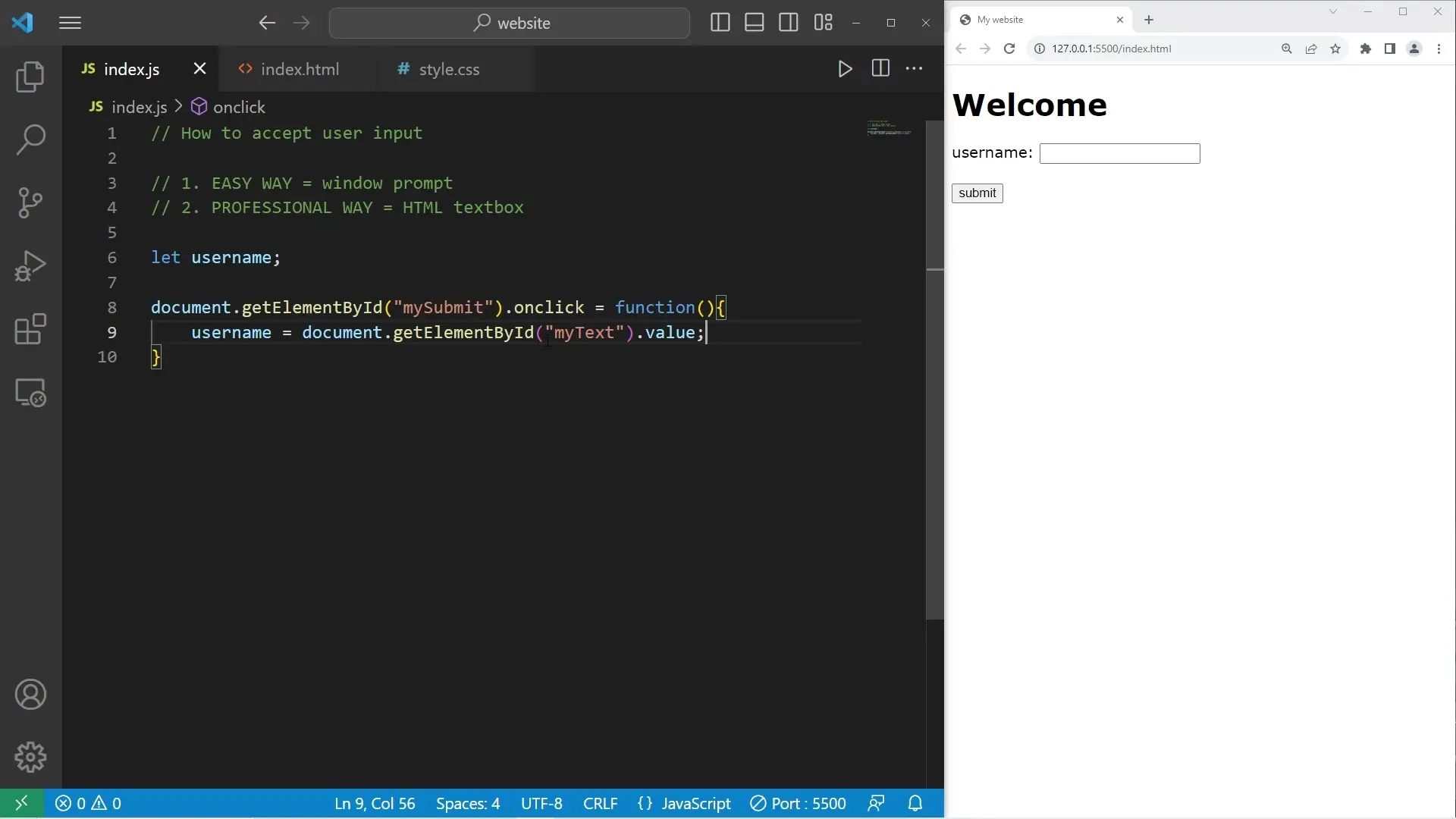
Next, we need to add JavaScript to handle the button click event and process the input:
// Declare the username variable
let username;
// Add event listener to the submit button
document.getElementById("mySubmit").onclick = function() {
// Get the value from the text input
username = document.getElementById("myText").value;
// Update the H1 element with a greeting
document.getElementById("myH1").textContent = `Hello ${username}`;
};When the user enters their username in the text box and clicks the Submit button, the JavaScript code captures the input value, stores it in the username variable, and updates the H1 element to display a personalized greeting.
When deciding which method to use for collecting user input, consider the following factors:
Once you've mastered the basics of collecting user input, consider these enhancements for your HTML form-based approach:
User input is a critical component of interactive web applications. JavaScript offers multiple ways to collect this input, from the simple window.prompt() method to more sophisticated HTML form elements with event handling. By understanding both approaches, you can choose the right technique for your specific project needs and user experience goals.
Whether you're building a quick prototype or a polished web application, mastering these user input techniques will help you create more interactive and user-friendly JavaScript applications.
Access our quantum knowledge cores and upgrade your programming abilities.
Initialize Training Sequence