
JavaScript Variables Explained: Master the Core Building Blocks of Programming
JavaScript Variables Explained: Understanding the Essential Building Blocks of Modern Programming

JavaScript is the programming language that transforms static web pages into dynamic, interactive experiences. Whether you're building a calculator, a form, or any modern web application, understanding JavaScript fundamentals is essential. This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know to start your JavaScript journey with confidence.
Before diving into JavaScript coding, you'll need to set up a proper development environment. Visual Studio Code (VS Code) is a popular choice among web developers due to its lightweight nature and extensive extension support.
The HTML file provides the structure for your web page. Start by creating a basic HTML template and linking your CSS and JavaScript files properly.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>My Website</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css">
</head>
<body>
<h1 id="myH1"></h1>
<p id="myP"></p>
<script src="index.js"></script>
</body>
</html>Notice that we've included empty H1 and paragraph elements with unique IDs. We'll use JavaScript to populate these elements with content. Also, the script tag is placed at the bottom of the body to ensure all HTML elements load before the JavaScript runs.
While our focus is on JavaScript, adding some basic CSS will make your page more visually appealing. Here's a simple example:
body {
font-family: Verdana, sans-serif;
font-size: 2em;
margin: 20px;
}
h1 {
color: #333;
}
p {
color: #666;
}Now let's explore the basics of JavaScript that will help you understand how to make your web pages interactive.
The console is a developer's best friend for debugging and testing. Use console.log() to output messages to the browser's console:
// This is a single-line comment
console.log(`Hello`);
console.log('I like pizza');
/* This is a
multi-line comment
that can span several lines */
To view these outputs, right-click on your web page, select 'Inspect', and navigate to the 'Console' tab in the developer tools.
Alert boxes create pop-up messages that users must acknowledge before continuing. While not commonly used in modern web applications, they're useful for learning purposes:
window.alert(`This is an alert`);
window.alert(`I like pizza`);Comments are crucial for documenting your code and making it understandable for yourself and other developers. JavaScript supports two types of comments:
One of JavaScript's most powerful features is its ability to dynamically change the content of HTML elements. This is done by selecting elements and modifying their properties:
// Select the H1 element by its ID and change its text content
document.getElementById('myH1').textContent = 'Hello';
// Select the paragraph element by its ID and change its text content
document.getElementById('myP').textContent = 'I like pizza';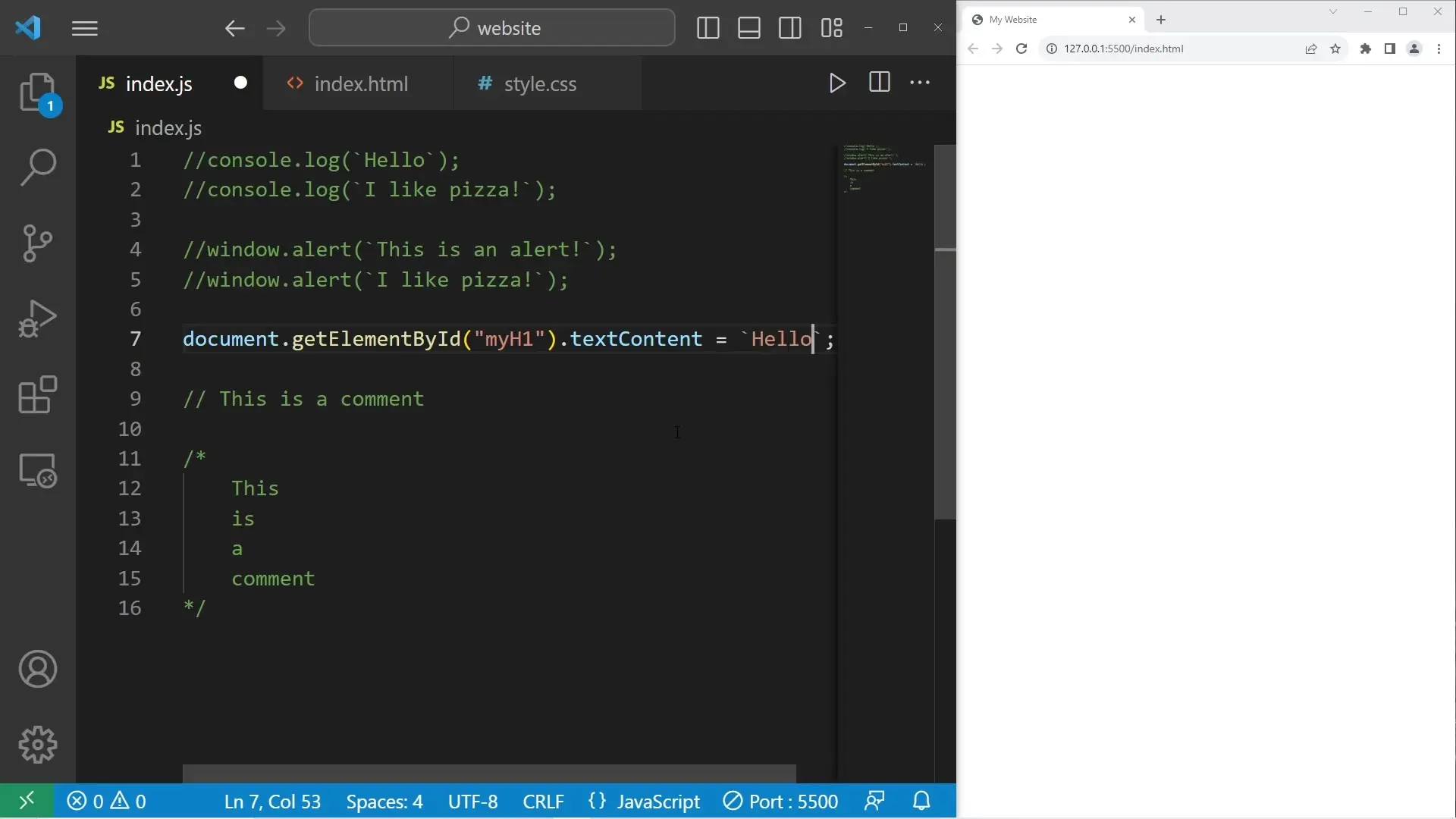
JavaScript offers multiple ways to work with text (strings). While you can use single quotes ('text') or double quotes ("text"), template literals (using backticks) offer more flexibility, especially when working with variables:
const name = 'World';
console.log(`Hello, ${name}!`); // Outputs: Hello, World!The ${} syntax within template literals allows you to embed expressions, including variables, directly within your strings.
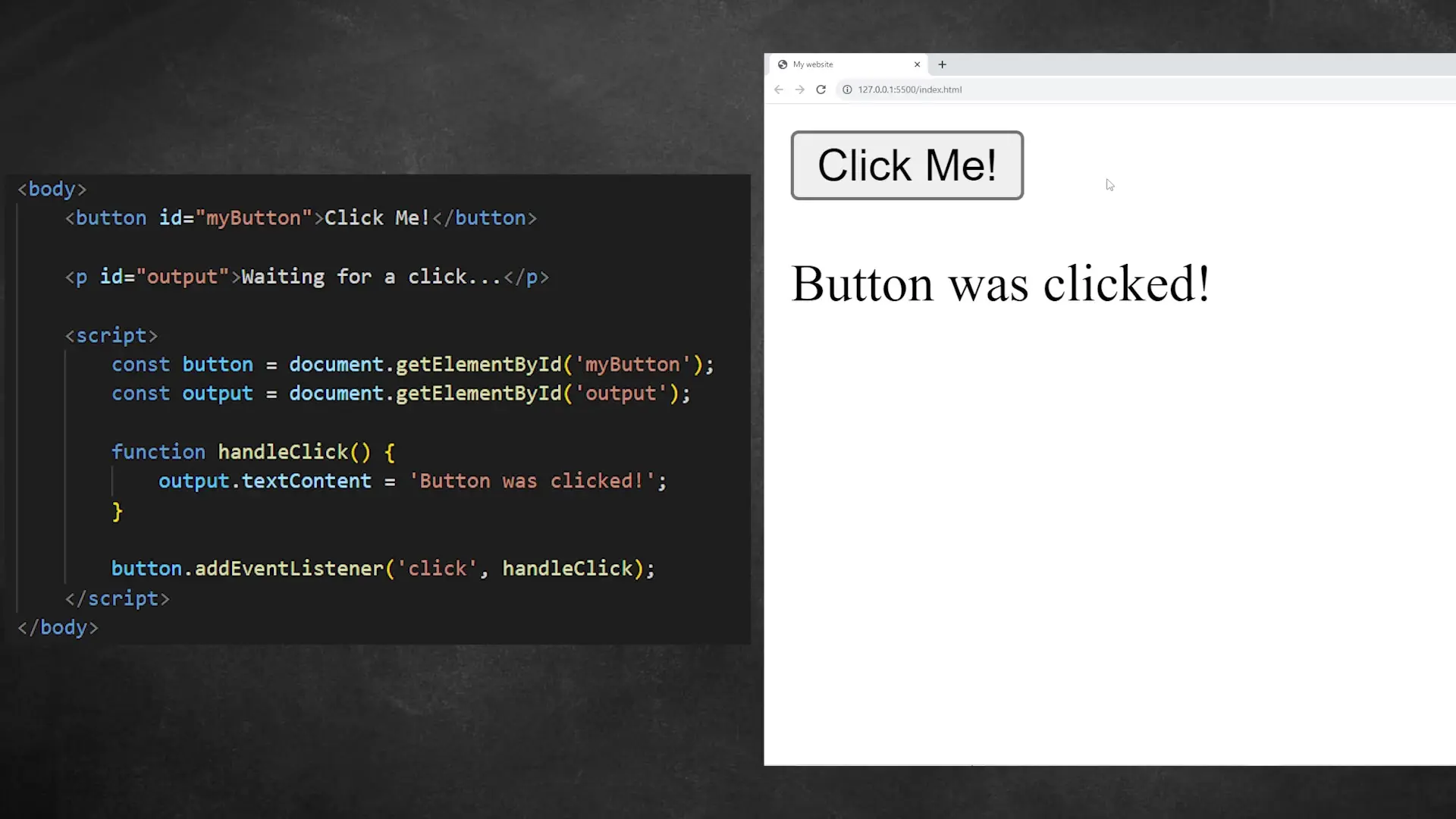
Let's combine what we've learned to create a simple interactive element. We'll create a button that changes text when clicked:
<!-- Add this to your HTML file -->
<button id="myButton">Click Me</button>// Add this to your JavaScript file
const button = document.getElementById('myButton');
button.addEventListener('click', function() {
document.getElementById('myH1').textContent = 'Button was clicked!';
document.getElementById('myP').textContent = 'JavaScript is awesome!';
});This code adds an event listener to the button. When clicked, it changes the text content of both our H1 and paragraph elements.
As you continue learning JavaScript, you'll want to explore these important concepts:
Remember that learning JavaScript is a journey that takes time and practice. Start with these fundamentals and gradually build your knowledge by working on small projects that interest you.
JavaScript is the language that brings web pages to life, enabling dynamic, interactive user experiences. By mastering these fundamental concepts, you've taken your first steps toward becoming a proficient web developer. Continue practicing, building small projects, and gradually tackling more complex concepts. With persistence and curiosity, you'll soon be creating sophisticated web applications that engage and delight users.
Access our quantum knowledge cores and upgrade your programming abilities.
Initialize Training Sequence