
React 19.2 has arrived with six impressive new features that significantly enhance the developer experience and application performance. These additions address common pain points in React development while introducing powerful new capabilities. Let's explore each feature and understand how they can improve your React applications.
1. Activity Component: A New Approach to Conditional Rendering
The new Activity component offers a superior alternative to traditional conditional rendering. Unlike the standard approach where components are completely unmounted when hidden, Activity preserves component state while maintaining performance.
Consider a sidebar with an uncontrolled input and expandable sections controlled by useState hooks. With traditional conditional rendering (using the ternary operator or && logic), when you close and reopen the sidebar, all state is lost because the component unmounts completely.
// Traditional conditional rendering
{isOpen && <Sidebar />}With the new Activity component, you can preserve component state while maintaining performance:
// Using Activity component
<Activity mode={isOpen ? 'visible' : 'hidden'}>
<Sidebar />
</Activity>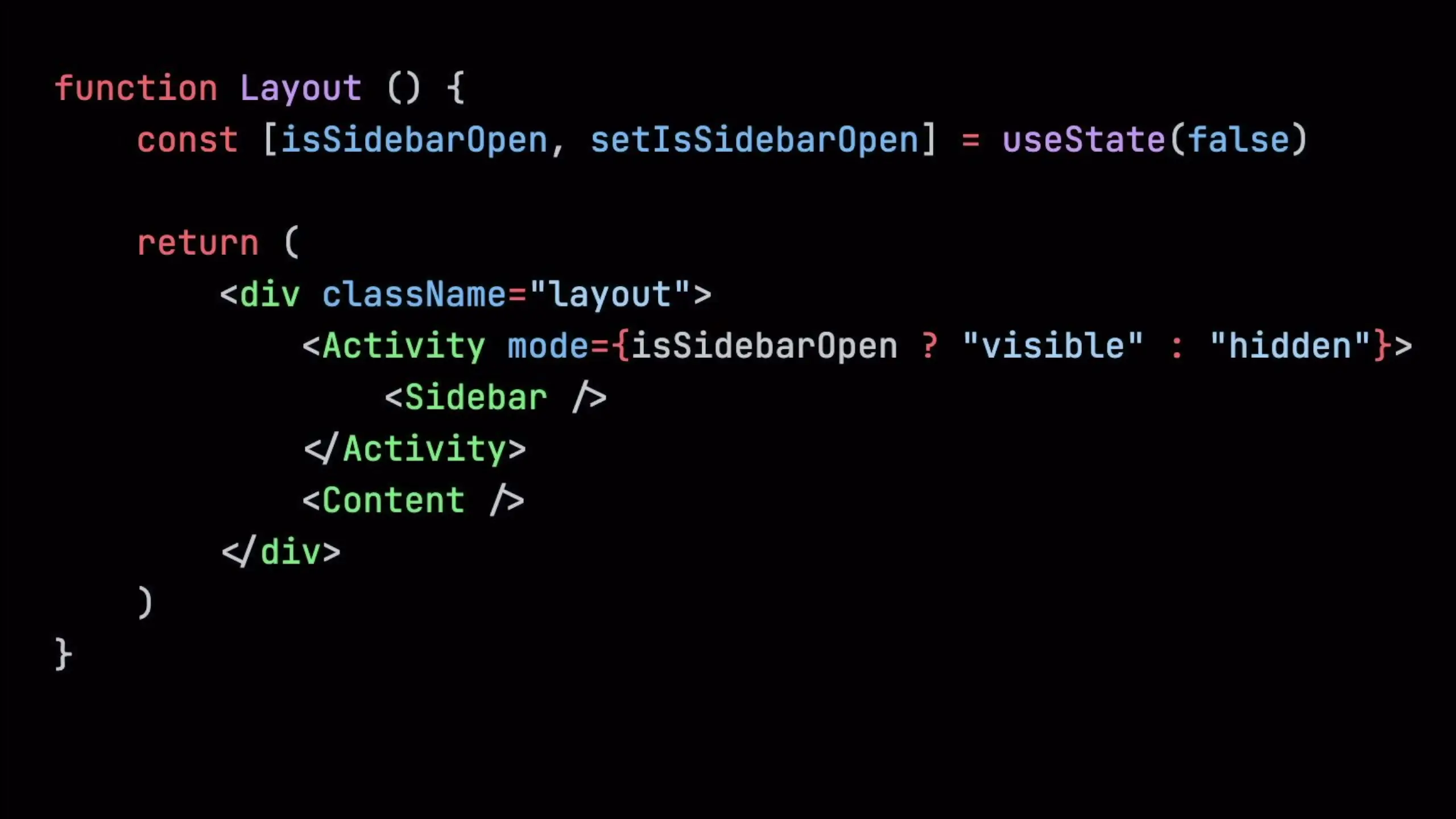
When the Activity component's mode is set to 'visible', it behaves like a normal component. When 'hidden', it applies CSS display:none to the DOM element rather than unmounting it. This preserves state values from useState hooks while still optimizing performance by unmounting effects and deferring updates.
This makes Activity perfect for pre-rendering scenarios. Components can be technically rendered without their effects running, enabling data fetching to occur in the background before a component is even displayed to the user.
2. useEffectEvent: Solving the Dependency Array Problem
The new useEffectEvent hook elegantly solves a common React dilemma: accessing the latest state values in effects without triggering unnecessary re-runs.
Consider this scenario: you want to log both a URL and a counter value 3 seconds after the URL changes. In previous React versions, you faced a difficult choice:
- Include counter in the dependency array: This causes the effect to restart its 3-second timer every time the counter changes
- Exclude counter from the dependency array: This violates React's rules of hooks and causes stale values
// The dilemma in previous React versions
useEffect(() => {
const timer = setTimeout(() => {
console.log('URL:', url, 'Counter:', counter);
}, 3000);
return () => clearTimeout(timer);
}, [url]); // If we exclude counter, we get stale values
// If we include counter, the timer restarts on every counter changeThe useEffectEvent hook solves this problem by allowing you to create a function that always sees the latest prop and state values without being included in the dependency array:
// Solution with useEffectEvent
const logValues = useEffectEvent((currentUrl) => {
console.log('URL:', currentUrl, 'Counter:', counter);
});
useEffect(() => {
const timer = setTimeout(() => {
logValues(url);
}, 3000);
return () => clearTimeout(timer);
}, [url]); // No need to include counter!This pattern is perfect for "effect events" - functions that need to be triggered by effects but should always have access to the latest state values.
3. Cache Signal: Optimizing Server Component Performance
For server components, React 19.2 introduces the cache signal feature, which helps optimize performance by preventing unnecessary background processing.
The cache function in React allows you to memoize expensive operations so that if multiple components call the same function with identical inputs during a render, React only executes it once. However, if React abandons a render (due to navigation or errors), those cached async functions might continue running unnecessarily in the background.
Cache signal provides an abort signal that changes to 'aborted' when React finishes with a render (whether successfully or not). This signal can be passed to async functions like fetch or database calls to stop them when React no longer needs their results.
// Using cache signal to optimize async operations
import { cache, cacheSignal } from 'react';
const fetchData = cache(async (id) => {
const signal = cacheSignal();
// The fetch will automatically abort if React no longer needs this data
const response = await fetch(`/api/data/${id}`, { signal });
return response.json();
});4. Performance Tracks: Enhanced DevTools Insights
One of the most valuable additions in React 19.2 is performance tracks - custom tracks in Chrome DevTools performance profiles that provide deeper insights into your app's performance without requiring React DevTools.
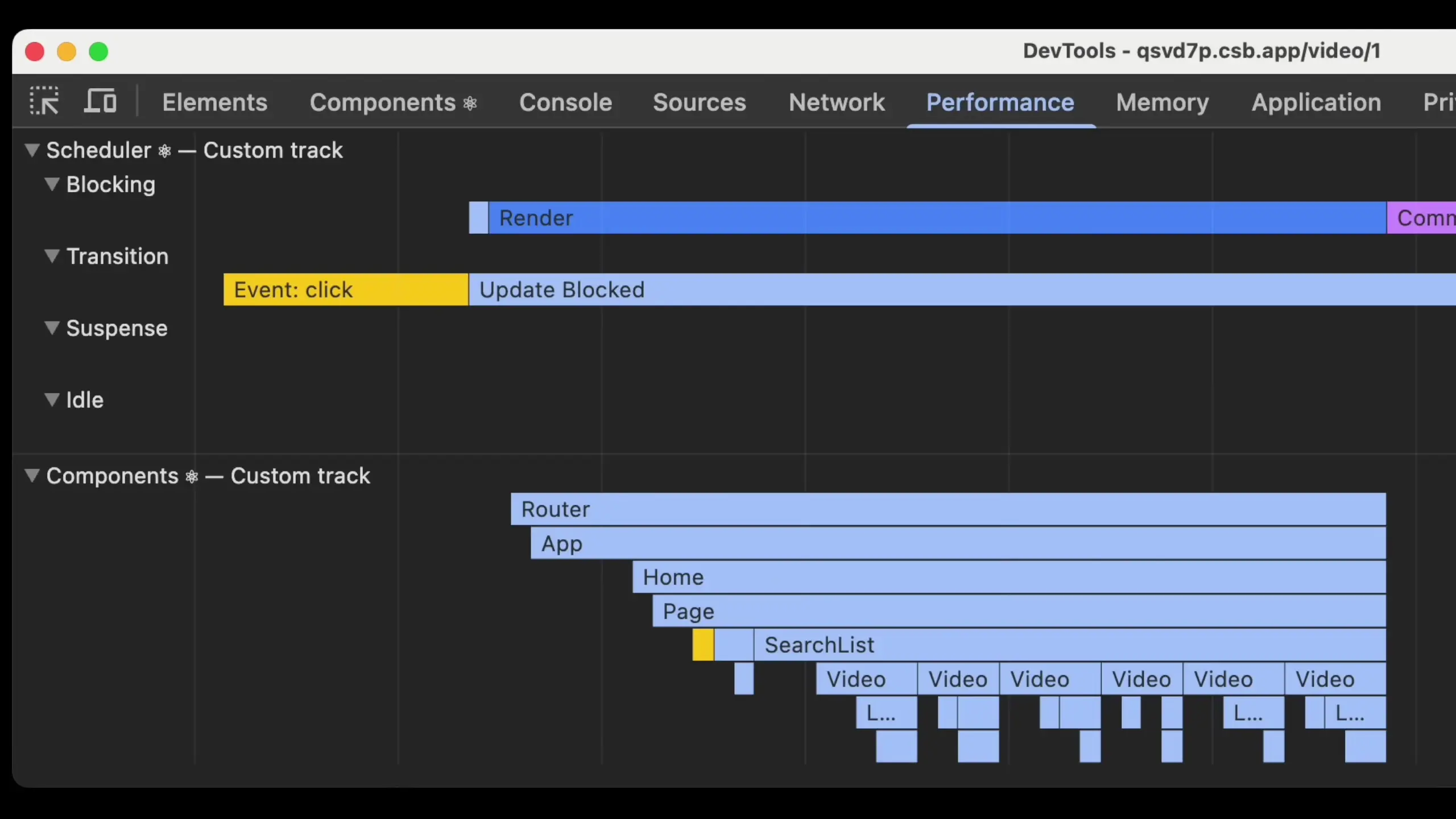
These new performance tracks include:
- Scheduler Track: Shows what React is working on across different priority levels (blocking for user interactions, transitions for updates inside startTransition)
- Components Track: Displays the tree of components React is working on, whether for rendering or running effects
Within these tracks, you'll see detailed labels such as 'mount' (when children or effects mount) or 'blocked' (when rendering is paused due to yielding to work outside React). This information helps you understand when components are rendered, when effects run, and the time each operation takes.
5. Partial Pre-rendering in ReactDOM
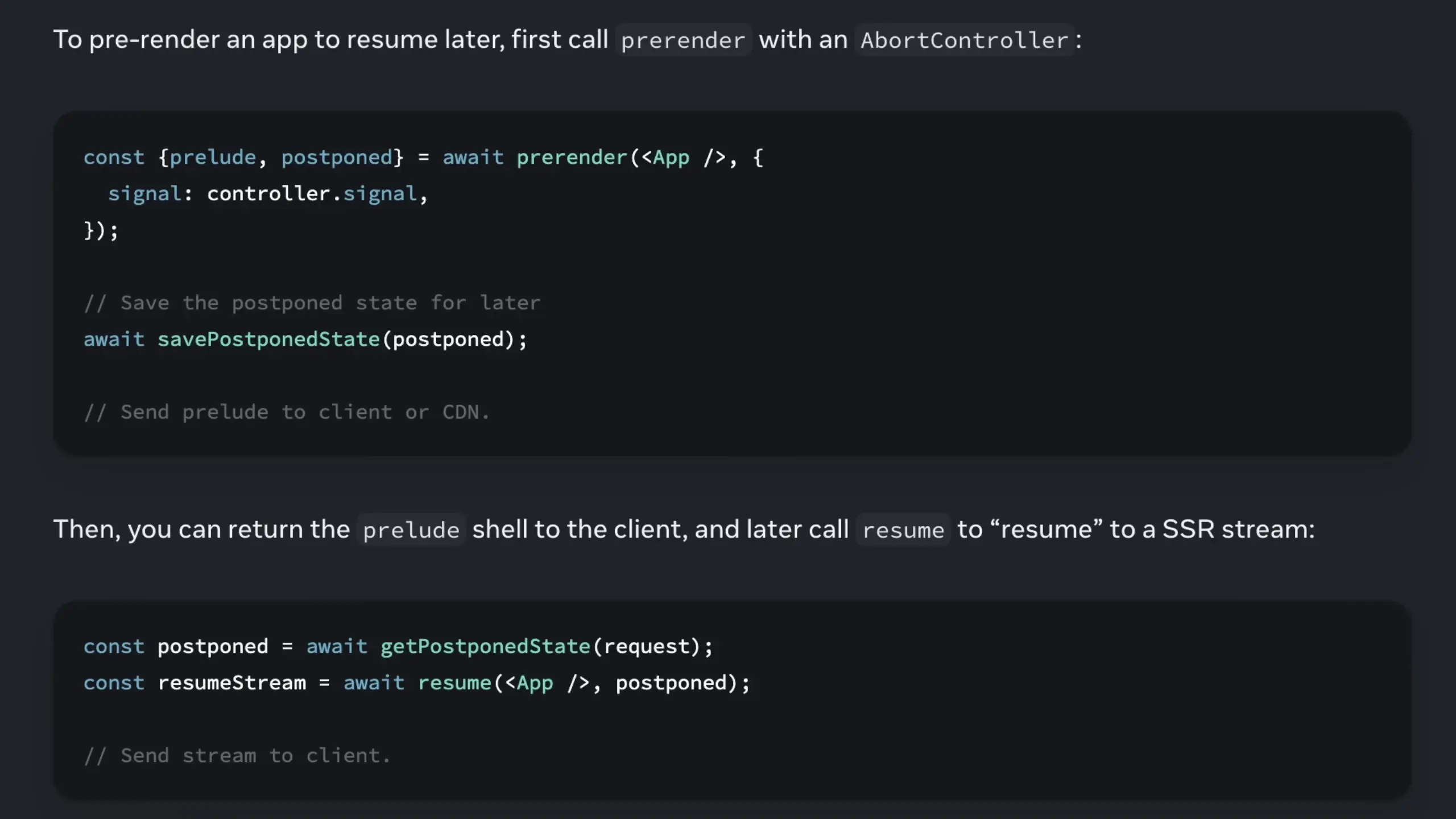
React 19.2 now includes built-in support for partial pre-rendering in ReactDOM. While this feature is primarily targeted at framework developers, it enables a powerful rendering strategy.
Partial pre-rendering allows your application to return a static "shell" (prelude) to the client first, then resume rendering to complete the rest of the content. This approach significantly improves perceived performance by getting content in front of users faster while the dynamic portions continue to render.
6. Enhanced ESLint Plugin with React Compiler Support
Finally, React 19.2 includes an upgraded ESLint plugin that supports the new flat config format and provides opt-in rules powered by the React compiler.
This plugin is increasingly important as following its rules ensures your codebase can fully leverage the React compiler's optimizations. The React compiler analyzes your code to automatically optimize rendering performance, and these linting rules help ensure your code is compatible with the compiler's capabilities.
Conclusion: Embracing React 19.2's New Capabilities
React 19.2 delivers substantial improvements that address real-world development challenges. From the Activity component's elegant state preservation to useEffectEvent's dependency array solution, these features demonstrate React's continued evolution toward better developer experience and application performance.
By incorporating these new features into your workflow, you can create more responsive, efficient, and maintainable React applications. The React team continues to focus on both developer experience and end-user performance, making this update a significant step forward for the framework.
Let's Watch!
6 Powerful New Features in React 19.2 That Will Transform Your Development
Ready to enhance your neural network?
Access our quantum knowledge cores and upgrade your programming abilities.
Initialize Training Sequence