
The rapid advancement of artificial intelligence has created a landscape where technology is outpacing regulation. While AI offers tremendous opportunities for innovation across healthcare, education, and government sectors, its current implementation by major tech companies raises serious concerns about data privacy and intellectual property rights. This article explores the critical challenges we face and potential solutions for a more ethical AI future.
The Current State of AI: Innovation vs. Exploitation
Artificial intelligence, particularly in its current form, has become a powerful tool for tech companies to extract value from user data. While the technology itself holds promise for transformative applications in healthcare, education, and public services, the reality is that most AI implementations today focus on profit maximization rather than societal benefit.
A recent 256-page bipartisan congressional report evaluated AI's impact on society, covering everything from healthcare and education to civil liberties and intellectual property. The findings highlight two particularly troubling areas: data privacy violations and intellectual property infringement.
The Data Privacy Crisis in AI Development
AI systems require massive amounts of data for training, creating significant privacy concerns. These models analyze vast datasets to identify patterns and produce instructions that can be applied to new data. The problem arises when this training data contains sensitive personal information that users never explicitly consented to share for AI development.
Major tech companies have been caught using customer data for AI training without clear consent. Google allegedly scraped Google Docs and Gmail content to train AI tools, while Twitter (now X) quietly updated its privacy policy to allow third-party collaborators to use user data for AI model training unless users specifically opt out.
The Federal Trade Commission has addressed this issue, stating that it may be unfair or deceptive for companies to adopt more permissive data practices while only informing customers through amendments to privacy policies. However, this acknowledgment falls short of creating meaningful protection for users.
The Consent Problem
The current approach to user consent is fundamentally flawed. Companies hide significant changes to data usage in lengthy privacy policies that most users never read. When these policies are updated to include AI training permissions, users typically aren't notified in a meaningful way.
For truly ethical AI development, companies should be required to obtain explicit, informed consent before using any user data for AI training. This consent should be presented in clear, simple language that a child could understand—not buried in legal jargon within a privacy policy.
Intellectual Property: The Creator's Dilemma
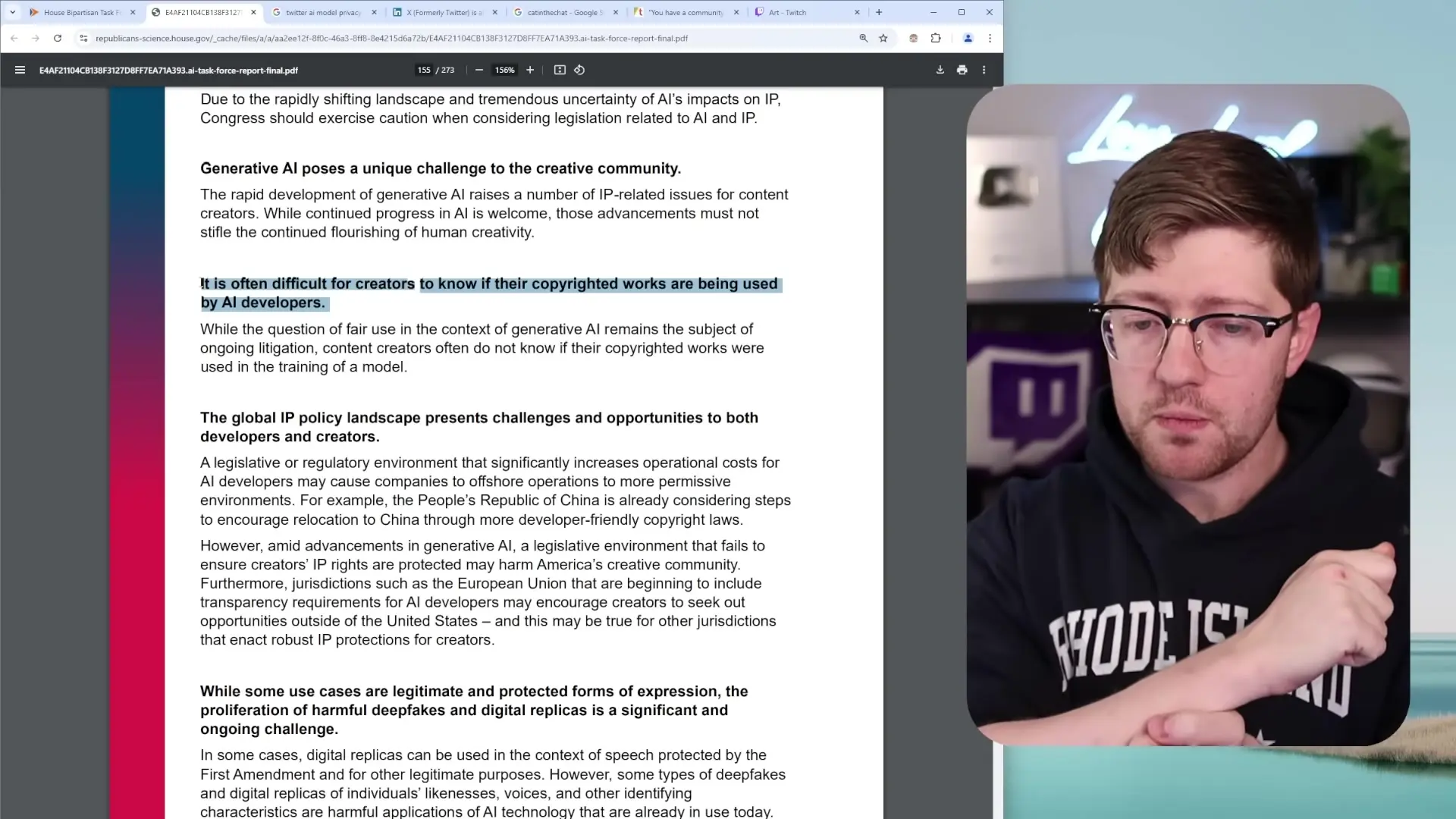
Perhaps even more concerning than privacy issues is how generative AI models are trained on creative works without permission or compensation to the original creators. This raises fundamental questions about intellectual property rights in the digital age.
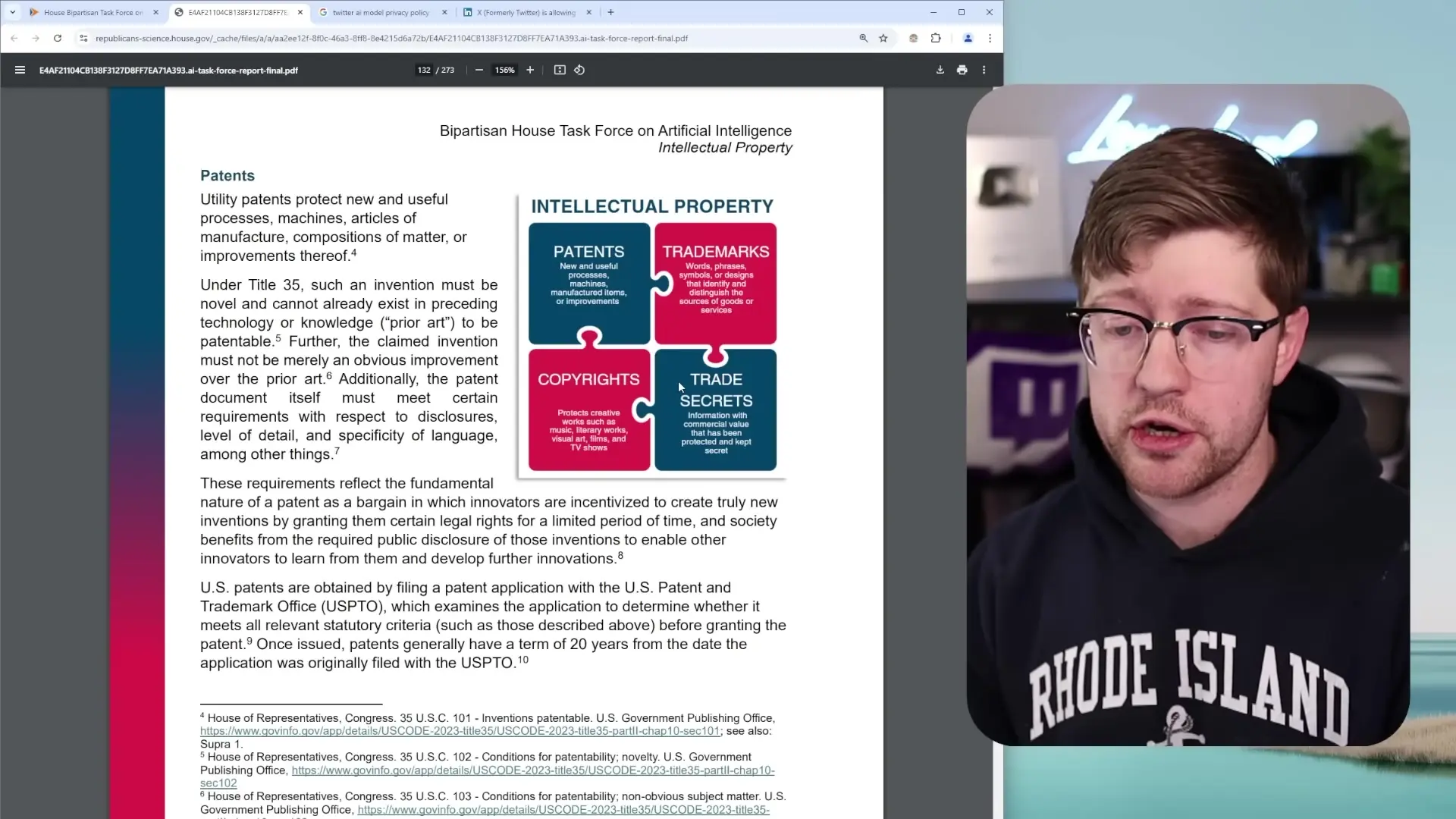
In the United States, intellectual property is protected through four primary mechanisms: patents, trademarks, trade secrets, and copyrights. The latter two are particularly relevant to AI development:
- Copyright protects original works of authorship during the creator's lifetime plus a limited time afterward
- Trade secrets include proprietary information with commercial value that companies take reasonable steps to protect
When AI companies scrape the internet for training data, they collect countless copyrighted works—art, writing, code, music—without permission from or compensation to the creators. This creates a situation where AI can generate content that mimics the style and substance of human creators, potentially devaluing their work and violating their intellectual property rights.
The Code Conundrum
For software developers, this issue extends to proprietary code. When developers use AI tools for code review or generation, they may inadvertently expose company trade secrets. There have been documented cases where AI models have reproduced specific code snippets from open-source projects in their responses, raising questions about whether these models are simply regurgitating training data rather than truly generating new content.
This creates a paradoxical situation where using AI for development might actually increase intellectual property risks rather than mitigating them.
The Path Forward: Balancing Innovation and Protection
While the challenges are significant, there are potential solutions that could help create a more ethical AI ecosystem that respects both privacy and intellectual property rights.
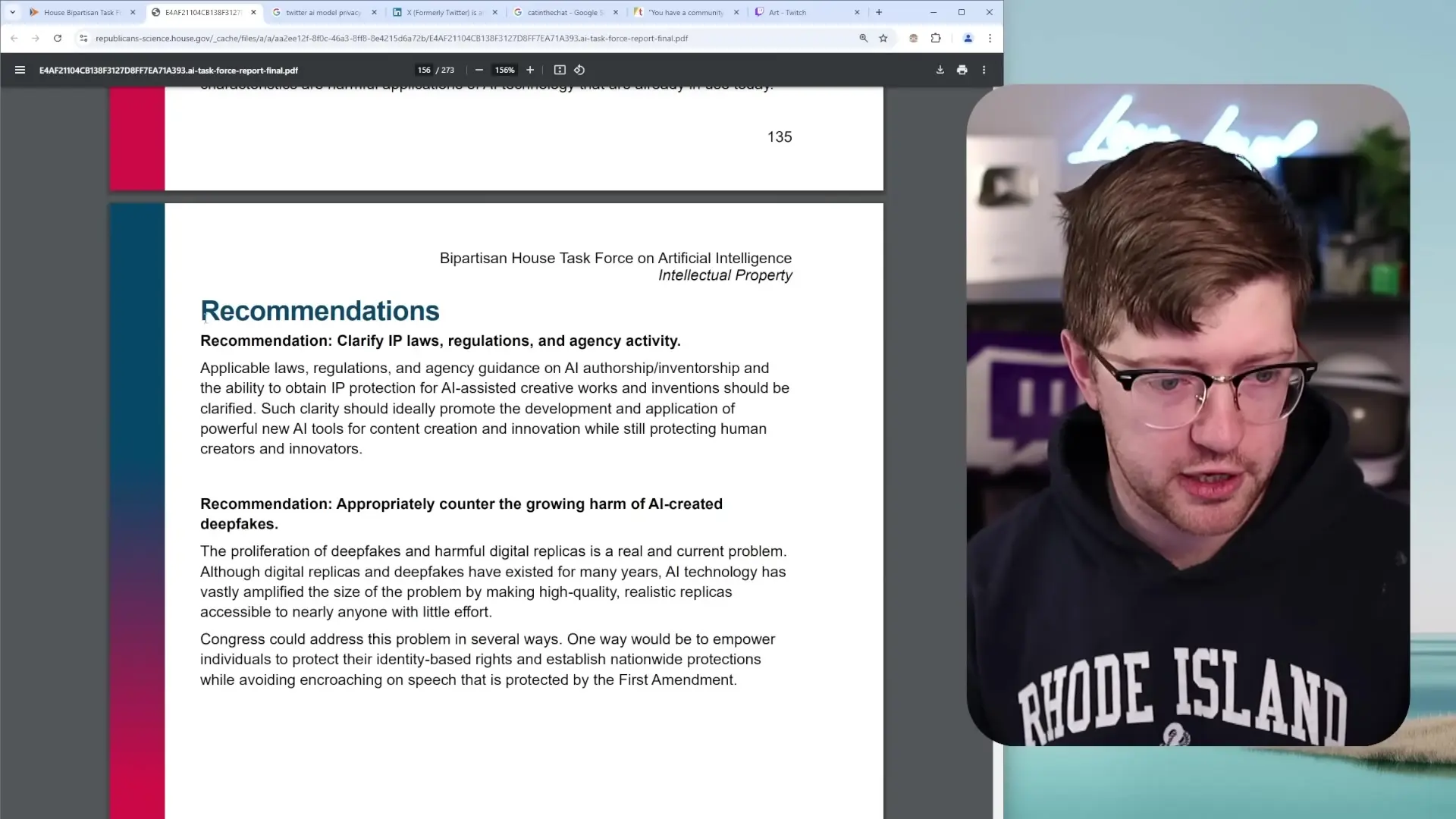
Recommended Policy Changes
- Require explicit, clear consent for AI training: Companies should obtain specific permission before using any user data for AI training, with simple, understandable explanations of how the data will be used.
- Establish opt-in rather than opt-out policies: Users should actively choose to participate in AI training rather than having to find and disable hidden settings.
- Create compensation frameworks for creators: Artists, writers, musicians, and other creators whose work is used to train AI should be fairly compensated.
- Clarify copyright law for AI-generated content: Legal frameworks need updating to address whether AI-generated works based on copyrighted material constitute derivative works.
- Mandate transparency in AI training data: AI companies should disclose what sources were used to train their models.
- Implement stronger data privacy regulations: Comprehensive privacy laws should protect users from unauthorized data collection and usage.
- Develop ethical AI certification standards: Independent verification of AI systems' compliance with privacy and IP standards could help users make informed choices.
The Future of AI: Opportunities and Challenges
Despite the current problems, artificial intelligence holds tremendous potential for positive impact. The technology could revolutionize healthcare diagnosis, personalize education, make government services more efficient, and solve complex problems across numerous domains.
However, realizing this potential requires addressing the fundamental challenges of data privacy and intellectual property protection. Without proper regulation and ethical guidelines, AI development risks continuing down a path that prioritizes corporate profits over creator rights and user privacy.
Conclusion: A Call for Balanced Regulation
The congressional task force report represents an important first step in addressing AI's challenges, but much more needs to be done. Effective regulation must balance innovation with protection, ensuring that AI development respects fundamental rights while still allowing for technological advancement.
For AI to truly benefit society, we need clear rules that protect both data privacy and intellectual property rights. This means requiring explicit consent for data usage, establishing fair compensation for creators, and creating transparency in how AI systems are trained and deployed.
The future of AI doesn't have to be dystopian. With thoughtful regulation and ethical development practices, artificial intelligence can fulfill its promise as a technology that enhances human capabilities rather than exploiting human creativity.
Let's Watch!
7 Critical AI Challenges Threatening Data Privacy and Intellectual Property
Ready to enhance your neural network?
Access our quantum knowledge cores and upgrade your programming abilities.
Initialize Training Sequence