
DeepSeek, a Chinese AI company that develops open source language models, recently made waves in the AI community by releasing not five, but eight powerful repositories during their open source week. With an estimated 84.5% profit margin from their current API traffic, DeepSeek's decision to share their core optimization code demonstrates a commitment to open source development that could significantly impact the entire AI industry.
The Business Impact of DeepSeek's Open Source Strategy
DeepSeek's open source initiative comes at a time when they're reportedly generating substantial profits from their R1 model - potentially up to 500,000 USD daily or approximately 200 million USD annually. During off-peak hours, they've reduced API prices by 50-75%, making their R1 model nearly 10 times cheaper than competing models like O3 mini.
What makes this open source release particularly significant is that DeepSeek isn't just sharing basic interface code. They're providing access to the very optimization techniques that contribute to their impressive profit margins - techniques developed by some of the industry's most talented engineers.
Day 1: Flash MLA - Optimizing Attention Mechanisms
The first repository DeepSeek released is Flash MLA (Multi-head Latent Attention), which builds on the concepts of Flash Attention but specifically optimizes DeepSeek's custom attention architecture proposed in mid-2024.
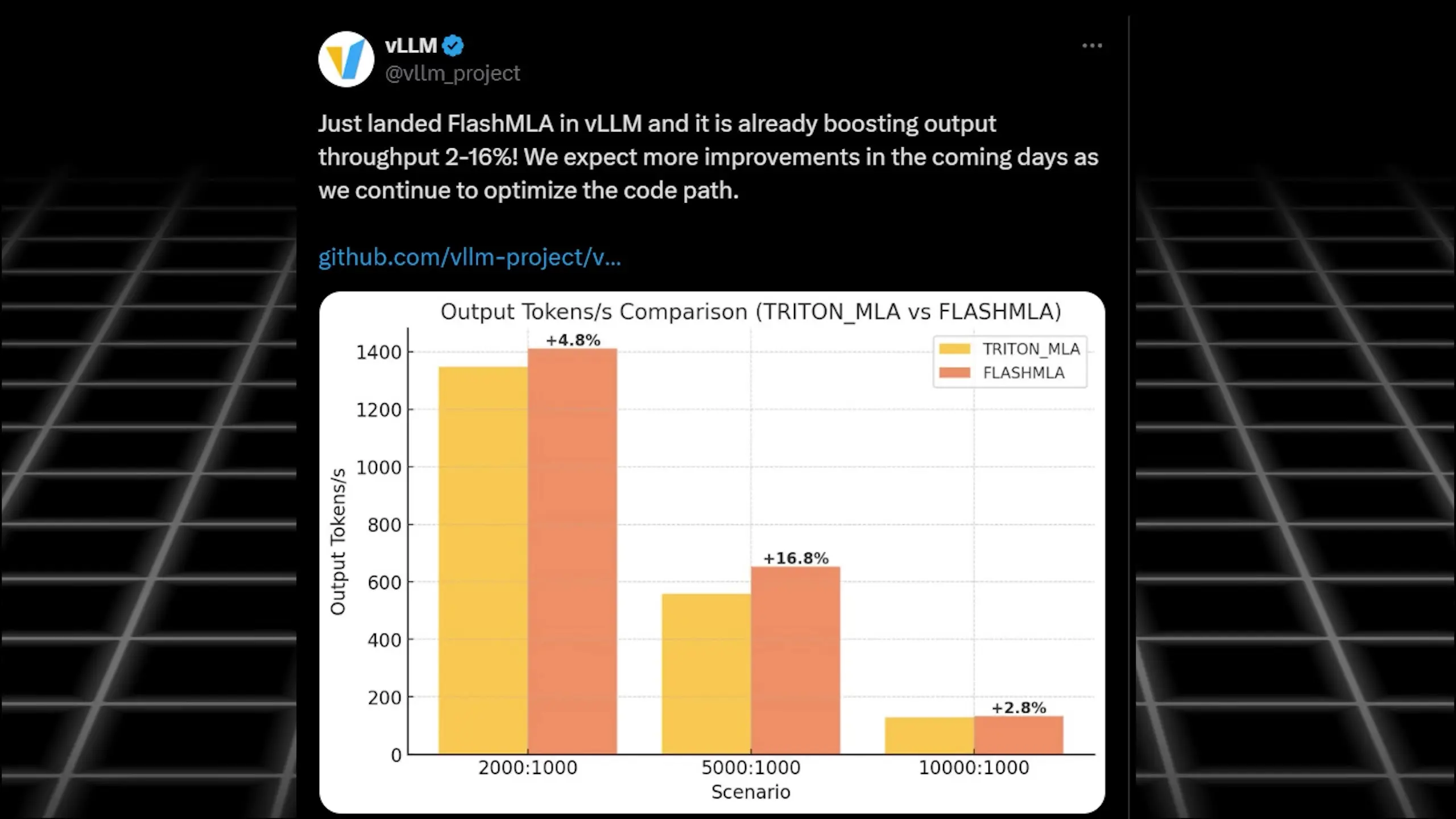
Flash Attention addresses a common bottleneck in AI processing: when models try to pass large inputs to the GPU all at once, they hit memory transfer limitations. By breaking inputs into smaller chunks for sequential processing, Flash Attention achieves up to 3x speed improvements without affecting output quality.
What sets DeepSeek's implementation apart is that it's written in CUDA rather than higher-level languages like Triton. This is comparable to the difference between precisely controlling every muscle movement versus giving general movement commands - CUDA offers maximum performance through precise control, while Triton sacrifices some efficiency for simplicity.
Day 2: DPP - Deep Expert Parallelism
The second repository, DPP (Deep Expert Parallelism), represents the first open source optimization library specifically designed for parallel execution of experts in Mixture of Experts (MoE) architectures.
MoE models offer computational advantages by activating only a subset of the model (specific "experts") during inference rather than the entire network. However, training these models efficiently has been challenging due to their architectural complexity and variants.

DPP provides comprehensive support for training, low-latency inferencing, and can adapt to both single-server and network-distributed environments. This enables researchers and smaller AI labs to implement expert parallelism without requiring massive infrastructure budgets.
The DeepSeek team even documented how they discovered performance improvements through undefined behavior in PTX (Parallel Thread Execution) - essentially exploiting unintended hardware behaviors to achieve faster processing. This level of optimization requires deep understanding of GPU architecture beyond what's available in official documentation.
Day 3: Deep GeMM - Optimizing Matrix Multiplications
On the third day, DeepSeek released Deep GeMM (Deep General Matrix Multiplications), which focuses on optimizing the fundamental matrix operations that underpin virtually all calculations in AI models.
Deep GeMM implements advanced techniques like warp specialization (assigning specialized tasks to different workers, similar to a factory line) and FFMA SAS interleaving (ensuring matrix operations overlap to keep the GPU constantly busy).
These optimizations deliver up to 2.7x speedup for specific matrix shapes and a significant 1.2x improvement for both model training and text generation tasks. Since these improvements occur at the lowest computational level, the efficiency gains compound throughout the entire AI pipeline.
Day 4: Dual Pipe and EPLB - Advanced Parallelism
DeepSeek released three repositories on day four, including performance logs and two code repositories: Dual Pipe and EPLB.
Dual Pipe implements bidirectional pipeline parallelism as described in the DeepSeek V3 paper. Traditional AI training follows a sequential process (forward pass for predictions, backward pass for learning), which inevitably results in GPU idle time, especially when using multiple GPUs.
- Pipeline parallelism typically divides operations into micro-batches and overlaps them across GPUs
- Dual Pipe takes this further by processing data simultaneously from both ends of the pipeline
- This approach significantly reduces GPU idle time by maximizing utilization
The EPLB tool complements Deep EP by addressing load balancing in expert parallelism for massive models. Since some experts are used more frequently than others, EPLB duplicates popular experts and keeps related experts physically close together (even on the same GPU) to optimize resource utilization.
Day 5: 3FS and Small Pond - World's Fastest Distributed File System
DeepSeek concluded their open source week with what might be their most valuable contribution: 3FS (Firefly File System), potentially the world's fastest distributed file system with a peak read throughput of 6.6TB per second.
Developed since 2019 and specifically optimized for AI workloads, 3FS prioritizes random read speeds to handle the high-volume, read-once nature of AI data processing. To put this speed in perspective, it's equivalent to downloading approximately 50 4K movies every second - far beyond what typical commercial distributed file systems can achieve.

To make 3FS more accessible, DeepSeek also released Small Pond, which uses 3FS through DuckDB (an SQL database) to manage petabyte-scale datasets while maintaining simplicity. Small Pond can organize 110TB of data in just over 30 minutes, achieving an average throughput of 3.66TB per minute.
The Impact on the AI Ecosystem
DeepSeek's open source week represents a significant contribution to the AI community, particularly for smaller organizations and researchers who may lack the resources of major AI labs. By sharing highly optimized code for critical AI infrastructure components, DeepSeek is helping to democratize access to efficient AI development tools.
These repositories could potentially enable more organizations to build and deploy large-scale models without the massive infrastructure investments previously required. The Chinese AI startup's approach stands in contrast to some Western companies that have been more selective about what they open source.
As open source models like DeepSeek R1 continue to challenge proprietary alternatives, these optimization tools may accelerate the development of competitive open source AI solutions globally. For developers and researchers working on language models, these repositories provide valuable insights into state-of-the-art optimization techniques that can significantly improve performance and reduce costs.
Conclusion
DeepSeek's decision to open source eight repositories of highly optimized AI infrastructure code demonstrates a significant commitment to advancing the field beyond their own commercial interests. From Flash MLA's attention optimizations to 3FS's record-breaking file system performance, these tools address critical bottlenecks in AI development and deployment.
For the broader AI community, particularly smaller organizations and research teams, these contributions could level the playing field and enable more efficient development of large-scale models without massive infrastructure investments. As the Chinese open source AI movement continues to gain momentum, DeepSeek's repositories may well become foundational building blocks for the next generation of AI systems worldwide.
Let's Watch!
How DeepSeek's Open Source Repositories Are Revolutionizing AI Development
Ready to enhance your neural network?
Access our quantum knowledge cores and upgrade your programming abilities.
Initialize Training Sequence