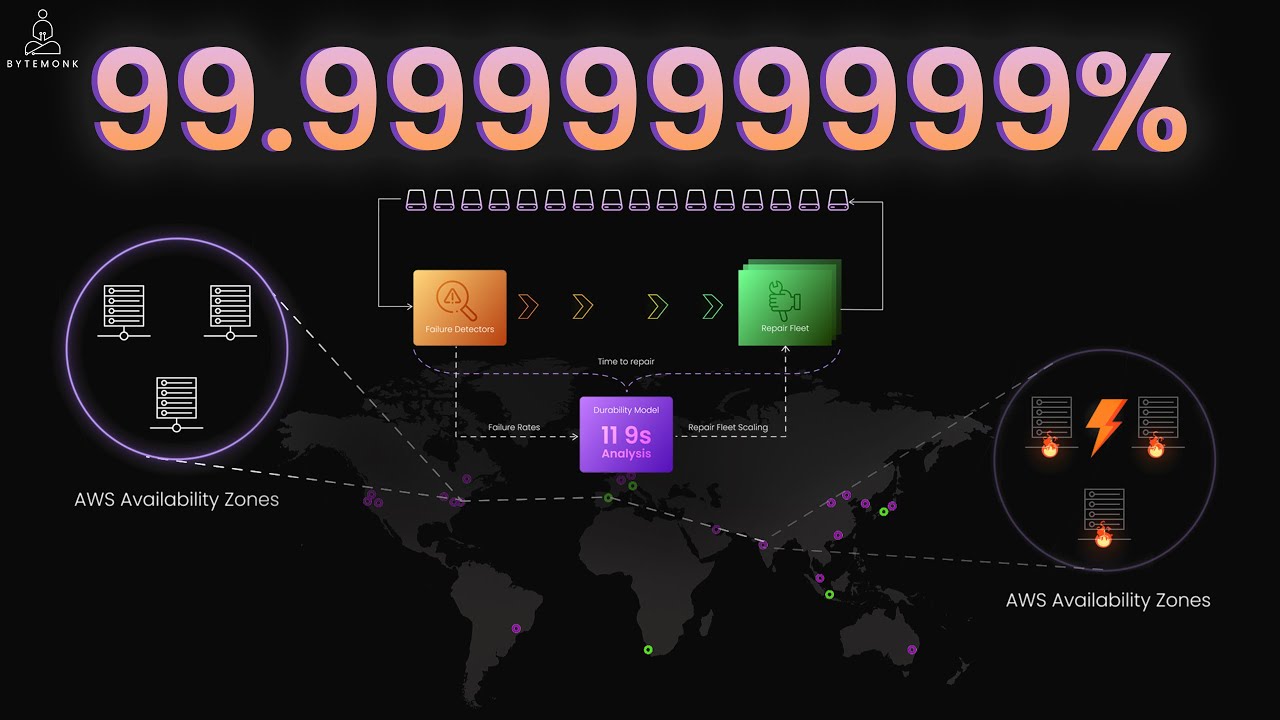
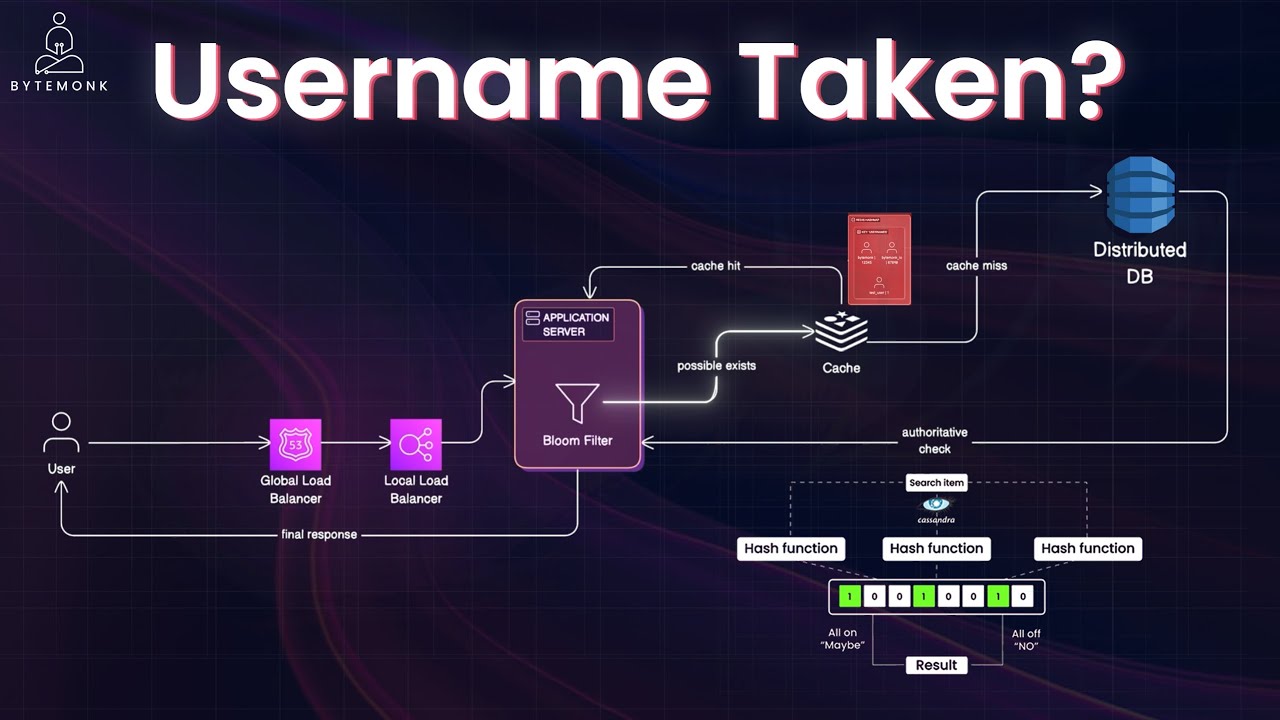
Database Architecture
Design principles, optimization strategies, and implementation patterns for SQL, NoSQL, and NewSQL database systems form the foundation of effective data management solutions across diverse application requirements. Database architecture decisions significantly impact scalability, performance, and maintainability, with each paradigm offering distinct approaches to handling data structure, consistency, and distribution patterns. SQL databases excel in scenarios requiring complex transactions and strict data integrity, leveraging normalization principles, query optimization techniques, and ACID properties to ensure reliable operations in environments where data relationships and consistency are paramount. NoSQL solutions—including document stores like MongoDB, key-value systems like Redis, column-oriented databases like Cassandra, and graph databases like Neo4j—prioritize flexibility and horizontal scalability, making them ideal for applications with evolving schemas, massive data volumes, or unique relationship modeling needs. NewSQL technologies combine SQL's transactional guarantees with NoSQL's distributed architecture advantages, using techniques like shared-nothing partitioning, consensus protocols, and distributed query processing to deliver high performance at scale while maintaining familiar relational models. Effective database implementation requires thoughtful consideration of access patterns, query optimization through proper indexing strategies, connection pooling mechanisms, and caching layers that reduce unnecessary database load. Performance tuning extends beyond initial design into ongoing maintenance practices, including regular monitoring of query execution plans, strategic denormalization when appropriate, and implementing data lifecycle policies that balance retention requirements with system performance. The most successful database architectures often employ polyglot persistence approaches, strategically leveraging multiple database technologies within a single application to address specific data access patterns and business requirements rather than forcing all data into a one-size-fits-all solution.